Others
DA-1726

- All rights for development and marketing of DA-1726 outside of Korea have been licensed out to NeuroBo Pharm (NASDAQ: NRBO).
Clinical unmet needs
- Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by excessive accumulation of fat due to an imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure.
- There are three main pharmacological strategies for obesity treatment: Suppressing appetite, Impairing absorption, and Increasing energy expenditure. Long-term use-approved drugs for weight management possess mechanisms that suppress appetite or inhibit fat absorption to control weight. However, there are currently no approved drugs with a mechanism that increases energy metabolism to induce weight loss.
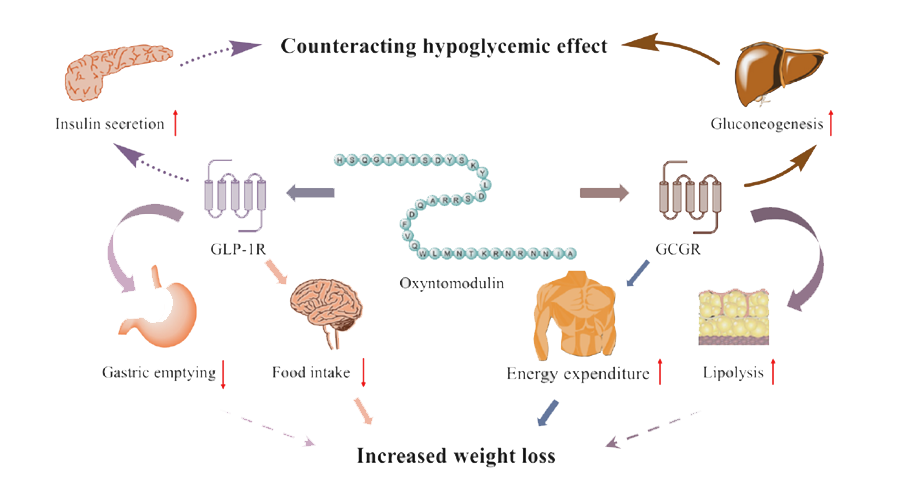
- Oxyntomodulin analogue can regulate body weight not only by suppressing appetite but also by increasing energy expenditure. Therefore, it is expected to be the next generation of obesity treatments with a mechanism that induces weight loss based on energy consumption, which can meet the unmet needs in the market.
MoA
(Mechanism of Action)
- Oxyntomodulin analogue
- Weight loss due to appetite suppression and energy expenditure increase through GLP-1 receptor and glucagon receptor activation
- Insulin secretion and glycemic control by activating the GLP-1 receptor
- Improvement of lipid metabolism via activation of GLP-1 receptor and glucagon receptor
- Superior weight loss: Delayed gastric emptying, appetite suppression, increased energy expenditure and lipolysis
- Effective glycemic control with low risk of hypoglycemia: Increased insulin secretion and gluconeogenesis