Oncology
DA-4507

Unmet needs
- The Kynurenine pathway has been identified as crucial mechanisms in cancer immune escape.
The conversion of Tryptophan into Kynurenine by IDO1/IDO2/TDO promotes the development of an immunosuppressive microenvironment and inhibits anti-tumor immune responses. - As Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) has emerged as a promising target for cancer immune therapy,
IDO1 inhibitors has been developed by a number of companies. However, the failure of a phase III clinical trial with the IDO1 inhibitor, Epacadostat, posed the need for in-depth insights into the Kynurenine pathway. - Several potential therapeutic targets have been investigated to overcome the limitation of IDO1 inhibitors.
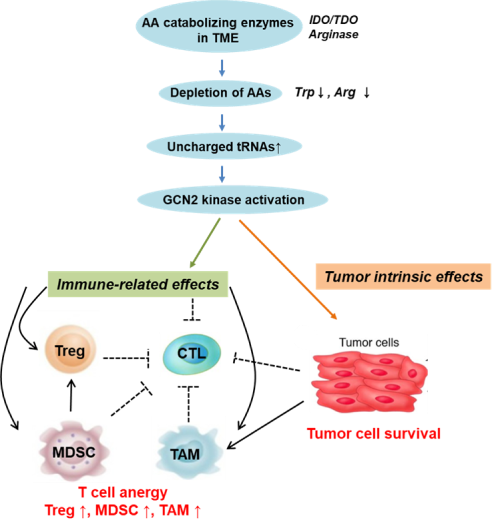
Among them, Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) and GCN2 could be attractive targets which are directly related with high level of Kyn and low level of Trp, respectively. We are anticipating that each of targets directly inhibits immunosuppressive effects within the tumor microenvironment(TME).
MoA
(Mechanism of Action)
- The inhibition of GCN2 (general control nonderepressible 2), a stress response kinase sensing
and modulating the response to nutrient deprivation, relieves T cell suppression and promote anti-tumor activity. Also, it regresses tumor growth by blocking the increase in the expression of essential amino acid synthase and transporters. - DA-4507, a novel small molecule GCN2 inhibitor, is a potent and selective in vitro.
Orally administered DA-4507 inhibits tumor growth in mouse syngeneic and xenograft tumor models. - Inhibition of GCN2 activity may provide a beneficial therapeutic option for cancer patients.