Oncology
DA-4515

Unmet needs
- Although there is significant interest in developing TEAD auto-palmitoylation inhibitors as cancer therapeutics, there are currently no such inhibitors approved for clinical use. TEAD auto-palmitoylation inhibitors is to overcome the limitations of existing cancer therapies and provide additional treatment options for cancer patients.
- Cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy and other targeted-therapies over time. TEAD auto-palmitoylation inhibitors may offer a new approach to targeting cancer cells that have become resistant to traditional treatments.
MoA
(Mechanism of Action)
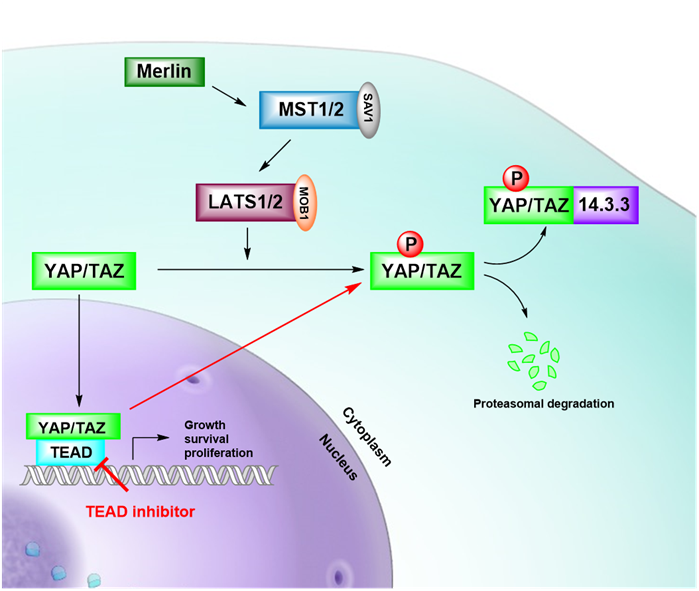
- The Hippo pathway plays a critical role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of this pathway is commonly found in many types of cancer. One of the key components of the pathway is the yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) which are regulated by a series of phosphorylation events mediated by upstream kinases.
- Recent studies have identified a new mode of regulation for YAP and TAZ, involving auto-palmitoylation of the transcription factor TEAD. TEAD is a transcription factor that interacts with YAP and TAZ to drive gene expression programs that promote cell growth and proliferation.
- Our TEAD auto-palmitoylation inhibitor works by specifically targeting the auto-palmitoylation process of TEAD, which is necessary for its interaction with YAP and TAZ. By inhibiting this interaction, our inhibitor leads to reduced transcriptional activity of the Hippo pathway target genes, resulting in decreased cell proliferation and tumor growth.